|
|
 |
Abnormal |
| |
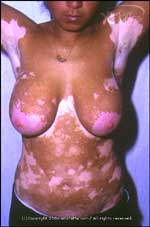
- Vitiligo is a skin
problem in which some areas of skin appear lighter than
others. It affects about 1% of the population.
|
 |
- The affected areas appear as "white" or "pale" patches of skin.
- Usually it does not cause any symptoms.
- It mostly affects the person's appearance cosmetically.
- However, these areas are more
sensitive to sunlight and burn easily, which may eventually
lead to skin cancer.
|
 |
- Vitiligo is due to a
problem with melanocytes, the cells in the skin that carry
color. In the regions where the skin is lighter, there is a
lack of these special cells.
|
 |
- Examination -- the doctor may easily recognize the typical "white patches" of discolored skin.
- If needed, a special light may be
used to examine the suspected area, or the doctor may choose
to examine a scraping of the skin under a microscope. If the
diagnosis is still not known, a biopsy may be in order.
|
 |
- Treatment for Vitiligo is
difficult. Treatment is primarily to help with the cosmetic appearance.
- Cosmetic makeup such as Covermark or Dermablend may be used to cover the "white" areas.
- If less than 20% of the skin surface is involved, a medicated cream with Methoxsalen may be applied and the area is exposed to ultraviolet light. The medicine is then washed off. People treated with this medicine must use a SPF 15 sunscreen when outdoors.
- If more than 20% is involved, Methoxsalen is given by mouth, followed by treatment with ultraviolet light. Patients must be careful outdoors, as severe sunburns may result from Methoxsalen use.
- This treatment is best for the face and chest. Fingertips and genital areas do not respond well.
- Years of therapy may be needed.
- Some patients have been treated with large doses of steroids to good effect.
- Newer, more promising surgical
treatments are being
studied.
|
 | |
|
 |
- Vitiligo has been seen more often in people with Hypothyroidism, Hyperthyroidism, diabetes, pernicious anemia, and Addison's disease.
- Skin cancers are more likely to develop with Vitiligo, so regular check ups with the doctor are advised.
- Areas of light skin are more sensitive to sunlight and should be protected with SPF 15 (or greater) sunscreen when exposed to the sun.
|
| | |
If you want your friend to read or know about this article, Click here
 |
|
|

