more about Thromboangiitis Obliterans
Also known as
Buerger’s disease
Description
 Normal |
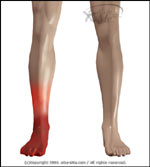 Abnormal |
- Thromboangiitis obliterans is also known as Buerger’s disease, and it is most often seen in young men who smoke. This disease causes blood circulation to the hands and feet to cut off, leading to pain, numbness, infections, and/or loss of the affected limb. Treatment is to stop smoking immediately and to take care of the limbs.
Symptoms
- All of the symptoms are due to the lack of circulation.
- People with this disease often have a history of Thrombophlebitis (inflammation and sometimes infection) of the superficial blood vessels in the limbs.
- The patient may have pain in his leg or calf that worsens with walking and improves with rest. However, if the disease is really advanced and the circulation is poor, he may experience pain in the limb even at rest.
- The patient may also have numbness, a burning sensation, or pain in the affected limb.
- In some, the foot or hand may be pale and cold, while others may have reddened skin.
- The pulse in the wrist, foot, and elbow may be decreased or absent.
- There may be skin ulcers on the hands or feet.
- Usually the patient has symptoms in both hands or in both feet, but not necessarily equally.
- The patient may also notice that his fingers or toes turn different colors (white, blue, and then red) when they are upset, or exposed to cold weather.
- The symptoms may come and go until the circulation is so poor that the patient starts to develop ulcers and eventually gangrene of the fingers or toes.
Cause
- The disease is caused by inflammation and blockage of some of the blood vessels in the body. It usually affects the arteries that supply the feet and hands.
- The cause of the inflammation is not known.
- It is seen most often in men under the age of 40 who smoke.
- It is common in Ashkenazi Jews from Eastern Europe.
- The symptoms of the disease are caused by blockage of the arteries, which leads to lack of circulation.
- The feet are more commonly affected than the hands.
How the diagnosis is made
- An examination usually reveals a decrease or absence of pulses in the extremities.
- Blood tests are usually normal.
- An angiogram (in which a dye is injected into the blood vessel and then X-Rays taken) may help with the diagnosis, and may rule out other causes.
Treatment
- The main treatment is to STOP SMOKING immediately. If the patient keeps smoking, then the disease will continue to proceed and become more severe.
- Once the patient stops smoking, then taking good care of the hands and feet is very important.
- If infections or ulcers develop, they must be treated very quickly and aggressively to prevent spreading.
- If the ulcers do not heal or if gangrene develops, then amputation may be necessary.
- In some people with the disease, they may need to have some of the nerves cut (sympathectomy) to help relieve the spasms of the blood vessel, and also to help relieve some of the pain.
- If people with this disease stop smoking soon enough and take good care of their hands and feet, then they may never need any amputation.
Similar Conditions
- Atherosclerotic disease
- Raynaud’s Disease
- Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome
- Cholesterol athroembolic disease
