|
|
 |
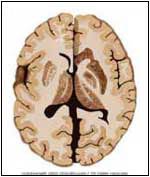
Normal |
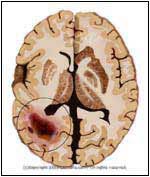
Abnormal |
|
|
- Brain tumors are either primary
(start in the brain itself) or from metastatic disease --
i.e., spread to the brain from a different area of the body.
Fifty percent of primary brain tumors are astrocytomas (made
up of cells called astrocytes), while the remainder is
comprised of more than ten other types. Brain tumors may be
benign or malignant (cancer).
- Here to follow is a (partial) list of the main types of possible brain tumors: acoustic neuromas (affect the 8th cranial nerve that deals with hearing), atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors, chondromas, chondrosarcomas, choroid plexus carcinomas and papillomas, chordomas, crainiopharyngiomas, cysts (e.g., arachnoid, colloid, dermoid, Epidermoid Cysts),
germ cell tumors, gangliomas, gliomas, ependymomas, and
other forms of
astrocytomas.
|
 |
- Decreased intelligence
- Headaches
- Nausea
- Emotional behavior
- Fatigue
- Seizures
- Many other symptoms develop according to
location:
- Hearing loss and a buzzing in
the ear with acoustic neuromas
- Vomiting, uncoordinated walking,
and drowsiness, are all associated with brain stem
tumors
- Problems with fine muscle
coordination (walking and speaking)
- Mental changes, personality changes, memory and judgment difficulties, Seizures, and one
sided-paralysis are symptoms with frontal lobe tumors
|
 |
-
Listed
below are some possible risk factors and causes that require
further research.
- Long standing Seizures
- Personality disorders
- About 5% of brain tumors are
thought to be hereditary (i.e., passed down from parent to
child)
- Individuals with tuberous
sclerosis, neurofibromatosis (type 1 and 2), familial
polyposis, and von Hippel-Lindau disease have a higher
incidence of brain tumors.
- Neurofibromatosis
- Genetic mutation or abnormalities
-- majority of individuals with glioblastomas may have
extra copies of chromosome number 7
- Petroleum industry workers
- Others such as weapons
manufacturers, pharmaceutical workers, farmers (exposed to
pesticides), those who work with synthetic rubber,
polyvinyl chloride, and nuclear power may also be at risk.
- Viruses are a possible cause that
is being investigated.
- Electromagnetic waves or low
frequency microwaves (EMF), cell phones, and power lines
are also being studied as possible risk factors.
- Some studies have shown that certain vitamins (A, C, E, and Folic Acid) may
reduce the risk of developing brain tumors in the children
of women who took the vitamins during pregnancy.
|
 |
- Dilated Pupils
- Papilledema (swelling of optic
nerve)
- Deficits depending on area of
tumor (e.g., if in motor area of brain)
- Paralysis
- Posturing (neurological term)
- Coma
- CT scan with contrast
- MRI scan with gadolinium
enhancement
- Electroencephalogram (EEG) may be performed to assess brain function and to check for Seizures.
|
 |
- Surgical removal of the tumor and/or radiation treatment. Chemotherapy (e.g., Methotrexate),
hormonal therapy (e.g., Tamoxifen or RU-486), biological
therapies (angiogenesis-inhibitors, such as Endostatin,
which stop new blood vessel formation in the tumor), and
gene therapy are some of the treatments being used and
researched for treatment of brain tumors. Ask your doctors
about ongoing new research and clinical
trials.
|
| | |
If you want your friend to read or know about this article, Click here
 |
|
|

