|
|
 |
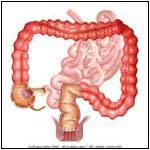
Normal |
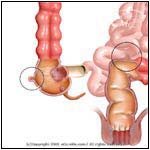
Abnormal |
| |
-
Diverticuli are outpouches located in the colon. Diverticulosis occurs when there are multiple diverticuli present in the colon. If these diverticuli become infected, it is known as diverticulitis. (See Diverticular Bleeding)
|
 |
- Abdominal pain
- Fever
- Nausea/vomiting may occur
|
 |
- Tenderness in the left lower abdomen
- Sometimes a mass is felt in the left lower abdomen
- Rectal exam may show microscopic or gross blood
- X-Rays to make sure the colon has not perforated
- CT scan of the abdomen/pelvis if the diagnosis is unclear
- Flexible Sigmoidoscopy and Barium Enema only after symptoms are improved (if these tests are done too early, they can cause a colon perforation)
|
 |
- Low-fiber diet; advance to high-fiber diet gradually.
- Antibiotics usually ciprofloxacin
and metronidazole by mouth
- No food by mouth so that the bowels may rest
- Intravenous fluids
- Nasogastric tube if an ileus is present (i.e., the colon is not working properly)
- Intravenous antibiotics
- Surgical treatment is required if the individual fails to respond to antibiotics.
|
 |
- Abscess (large
walled-off pus collection in the abdomen)
- Fistulas -- abnormal tracts between the colon and other organs such as the bladder
- Peritonitis -- infection of the
fluid in the lining over the abdomen
- Colon stricture (scarring)
- Colon Obstruction
|
| | |
If you want your friend to read or know about this article, Click here
 |
|
|

