|
|
 | |
Gallstone
disease
|
 |
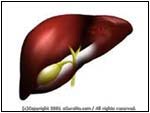
Normal |
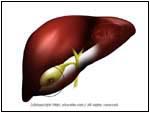
Abnormal |
| |
- The gallbladder is a small pouch
that sits on top of the liver where excess bile is stored.
Bile is a substance that the body uses to help digest fatty
foods.
- Gallstones occur when the bile in
the gallbladder becomes over concentrated (they precipitate
out like the salt crystal lab experiments done by children
in grade school) and form "stones" or crystals in the
gallbladder or bile ducts.
- Gallstones are predominantly of two types: 1) cholesterol (80%) and 2) Calcium bilirubinate
(20%). When the crystals are located in the bladder itself,
the condition is called cholelithiasis; when they are
located in the bile ducts, the condition is called
choledocholithiasis.
|
 |
- Often none
- Pain in right upper
abdomen
|
 |
- If there are no symptoms, treatment is unnecessary,
except if the patient is diabetic. Diabetics with gallstones
usually need them removed because they are at risk for
sudden, severe infections and perforations of the
gallbladder wall.
- If you have symptoms of recurrent severe pain despite diet changes, and diagnosis has been confirmed through X-Ray or ultrasound:
o Laparoscopic cholecystectomy may be
performed in which the gallbladder is removed via a special
technique using a camera scope inserted through an incision
in the abdominal wall; or via open laparotomy (open surgical
procedure).
- Ursodeoxycholic acid-a medication that dissolves some
cholesterol stones. It usually works very slowly (two years
or longer with side effects, and therefore is rarely
used).
- Chenodial and other medications are also being used to
dissolve the stones.
- Sonic Shock
waves
|
 |
- Cholecystitis/cholangitis-gallstones cause inflammation
and infection of the gallbladder or ducts leading to the
gallbladder. (See cholecystitis/cholangitis section.)
- Pancreatitis-gallstones may pass though ducts into pancreas, causing blockage and inflammation.
|
| | |
If you want your friend to read or know about this article, Click here
 |
|
|

